Why do joints hurt? Many patients go to the doctor with such a question or try to find the answer on their own. Unfortunately, this complaint is not specific and may indicate a pathology with different mechanisms and causes of development.
We will try to identify the most common causes of joint pain and learn how to treat common diseases.
Symptoms
Before immediately analyzing the causes of pain, it is worth learning more about the symptoms of diseases of the musculoskeletal system. A doctor who starts a diagnostic search will learn exactly how the joints hurt - so the specialist will quickly find the cause of the disease.
Depending on the nature of the feelings, there may be pain:
- It hurts.
- Cutting.
- Explosion.
- Compressive.
It differs in the intensity of pain in the joints of the arms and legs. Painful, weak pain indicates chronic diseases. If the joints are very painful, the senses do not allow you to move, then the process is sharp.
The rhythm of pain
Symptoms of all diseases of the joints of the hands and feet can be divided according to the rhythm of pain: mechanical or inflammatory. Mechanical pain has the following characteristics:
- It grows in the evening.
- Morning stiffness is not typical.
- It feels strong after training.
- Pain during rest or disappears completely.
- Onset - a certain type of pain during the onset of movement.
Inflammatory rhythm is characteristic of synovitis of the joints of the arms and legs of various origins. Symptoms include:
- Morning stiffness of more than 30 minutes on certain parts of the body or arms and legs.
- The pain increases early at night and in the morning.
- With exercise, the symptoms become less intense, and the stiffness of the body decreases.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs work well in this rhythm of pain caused by stiffness and pain in the body.
Other symptoms
Pain in the joints of the arms and legs, depending on the cause of development, is accompanied by certain manifestations. Why joint pain can often be identified by additional symptoms:
- Limited movement of arms or legs.
- Stiffness of limbs.
- Swelling in the joints of the arms and legs (swelling in the elbow joint).
- Local fever and redness of the skin.
- General weakness, fever.
- Skin lesions on the arms, legs, torso.
- Manifestations from other organs.
Depending on what symptoms are accompanied by pain in the joints of the arms and legs, the doctor will determine why the disease occurs.
Diseases of the joints

Pain in the joints of the arms and legs can be caused by diseases that are completely different in origin and mechanism of development. However, the most common causes of such symptoms can be identified:
- Osteoarthritis is a degenerative disease of cartilage and bone tissue. Pain in the joints is mechanical, combined with an inflammatory component during exacerbation.
- Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease in which the immune system attacks the joint by the body's own cells. Joint pain has an obvious inflammatory rhythm.
- Reactive arthritis is an inflammation caused by an infection in another organ. It often occurs with hepatitis and urinary tract infections.
- Infectious arthritis is associated with the joint entry of microbes.
- Injuries and fractures. Diagnosis is not difficult due to a history of trauma.
- Damage to ligaments and intraarticular formations. When the soft structures of the joints are damaged, it causes joint pain.
- Rheumatic diseases. A large group of causes of autoimmune damage to the joints: systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatism, Bechterew's disease, Reiter's syndrome and others.
- Gout and other metabolic arthropathies. Symptoms of musculoskeletal system damage are often associated with the deposition of various pathological substances in the joints. In gout, they are salts of uric acid.
- Psoriatic arthritis - the cause of this disease is unknown. Your body's antibodies affect the tissues of the joints, internal organs and skin. The most common manifestation of the disease is dermatitis - peeling of the skin on the extensor surfaces of the extremities.
This list reflects the most common causes of musculoskeletal disorders.
Joint pain can also be caused by vascular disease and neurological diseases. The attending physician must determine the final cause.
Diseases of the knee joints
Knee pain is one of the most common complaints reported to a rheumatologist. Why does my knee hurt? This element of the musculoskeletal system withstands large loads on the whole body on a daily basis, performs a wide range of motion and has a complex structure.
The knee joint suffers from various diseases, some of which are already listed above, others are specific to this joint.
"Knee hurts: how to get rid of it? " - First of all, consult a doctor. Instrumental diagnosis helps to understand why the knee hurts, but a probable diagnosis is made based on complaints and examinations.
Pain in the knee joint most often occurs for the following reasons:
- Gonarthrosis - arthrosis of the knee joint. This cause is the most common mechanism for knee pain. Articulation is exposed to daily loads, which is a major risk factor for osteoarthritis.
- Meniscopathy. The meniscus is the layers of cartilage inside the joint. These are the structures that are most often damaged when a knee injury occurs. With meniscopathy, the joints are severely damaged and pain occurs when you try to move. Treatment of pathology is operative.
- Arthritis of various origins. Pain in the knee joint with arthritis is inflammatory in nature, they may be associated with infection of the joint itself or another organ. Pain in the knee joint can also occur with rheumatoid arthritis and other autoimmune diseases.
- Gut. The knee joint is not the most common localization of gout arthritis. However, this joint can still be affected by the disease. Pain in the knees is accompanied by the presence of subcutaneous tofin, an increase in uric acid levels in the blood.
- Inflammation of tendons - tendonitis. Pain in the knee joint is often associated with soft tissue damage. When microtrauma occurs in a tendon or ligament, pain occurs in the knee, which is associated with a local inflammatory reaction. Symptoms are aggravated by exercise.
- Circulatory disorders. Vascular thrombosis, thrombophlebitis, varicose veins can cause pain in the knee. These problems often occur in postmenopausal women, as well as in people who frequently strain their joints.
- Baker's cyst and other diseases of the joint capsule. The knee joint has a complex structure, its synovium has folds and pockets. Knee pain can be caused by local inflammation of the joint capsule or accumulation of inflammatory fluid in the popliteal cavity.
- Tumors. Neoplasms rarely affect the articulatory area. The most common knee pain associated with tumor growth occurs when the joint metastasizes from another organ. In this case, the diagnosis is clear, and oncology is already being treated.
With these and other ailments, a person's knees ache, and the attending physician will tell you what to do in a particular situation.
Knee pain is not always a sign of a serious pathology, but it is not an extreme concern for your health.
Diagnostics

Before prescribing treatment for joint pain, your doctor must make a definitive diagnosis. To do this, he will perform several mandatory diagnostic procedures. The questionnaire standard includes the following:
- A general analysis of blood and urine will show the presence or absence of an inflammatory reaction.
- Biochemical blood test - assesses the function of the liver and kidneys, the state of protein, fat and carbohydrate metabolism.
- Radiography of the affected joints. X-ray is performed in several projections and allows to detect bone pathology.
Unfortunately, in most cases, the listed research methods are not enough to make a diagnosis. In this case, additional methods are used:
- Computed tomography - allows you to detect even the slightest damage to bone tissue.
- Magnetic resonance imaging - the method perfectly visualizes all soft tissues, including ligaments and menisci, tumors, cysts and other pathological formations.
- Ultrasound of joints - detects abdominal and solid pathological formations, can measure the speed of blood flow in the vessels.
- Arthroscopy is the insertion of a chamber into the joint space. One of the most accurate research methods.
- Diagnostic puncture - a fluid is drawn from the articular cavity into the syringe being examined.
These diagnostic tools allow you to make a correct diagnosis with a high probability. Many procedures are expensive or have contraindications, so the need for research is determined individually.
Treatment
How to treat joints? There are many tools, techniques and folk recipes for joint pain. The attending physician will help you choose the right therapy.
All the means and methods of therapeutic effects can be divided into several groups, each of which will be discussed below.
Drug treatment
Medications for joint pain are often used alone. This is not the right approach, it is better to use a complex treatment. However, drugs play a key role.
The most commonly used drugs:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Non-narcotic and opioid analgesics.
- Muscle relaxants.
- Glucocorticosteroids.
- Chondroprotectors.
- Cytostatics.
- Vitamins.
The attending physician should explain to the patient what each specific medication helps.
Other drugs are prescribed for vascular diseases. If you have vascular disease of the lower extremities, and at the same time have pain in the joints of the legs, the attending physician decides what to do and what treatment to choose.
Physiotherapy
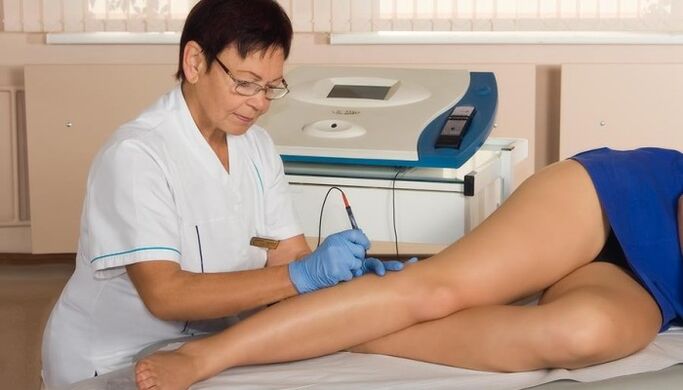
The use of various physiotherapeutic procedures complements medical treatment.
The following methods help with joint pain:
- Electrophoresis.
- Phonophoresis.
- Acupuncture.
- Paraffin applications.
- Rhodon baths.
- Mud therapy.
- Magnetotherapy.
These and other methods allow to increase blood flow in the affected joint, eliminate swelling and increase the intensity of metabolic processes.
Therapeutic immobilization
Therapeutic immobilization is often prescribed for acute joint pain. This method involves wearing a bandage, corset and orthosis on the injured joint.
You can not use the bandage for a long time, because under the orthopedic design, the muscles atrophy from immobility. However, support from immobilizing products is very useful during heavy loads.
exercise therapy

Physiotherapy plays a key role in the treatment of any pathological process occurring in the musculoskeletal system. Gymnastics allows the joint to adapt to the load, restore muscle strength, improve blood circulation and eliminate swelling.
The intensity and timing of exercise largely depends on the nature and severity of the disease. Exercises should begin with breathing exercises and warming up of small muscles.
20-30 minutes of morning exercise a day should be complemented by swimming, Nordic walking and other aerobic activities.
Massage
Massage procedures perfectly relieve the patient of joint pain. What is the massage method used for? The procedures increase blood circulation, eliminate swelling and reduce pain. You should entrust the implementation of this procedure to a specialist and undergo a massage after performing a series of exercises.
Surgery
Surgery is the main and sometimes the only role in the treatment of articular pathology. Thus, the consequences of injuries, severe degenerative diseases, complications of articular pathology are treated.
The operation can be performed in different volumes: from plastic to prosthetics of damaged joints. The instructions for the intervention are determined by the patient's attending physician in conjunction with the surgeon or traumatologist.
Treatment with folk remedies

Traditional medicine recipes are still popular in our country. It should be noted that folk remedies are not a proven and proven method and are used by patients at their own risk and peril.
The following folk remedies are used to treat pathology of the musculoskeletal system:
- Bay leaf and cabbage compresses.
- Decoctions of sunflower root.
- Golden mustache ointment.
- Apply into egg shell.
- Compresses of crushed chestnuts.
- Rye grains and other grain structures in the form of decoctions.
- Boiled rice.
- Baking soda.
If you decide to use one of the traditional medical prescriptions, consult your doctor first.

























